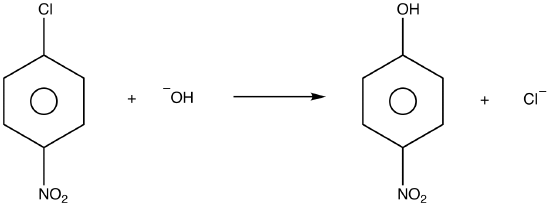
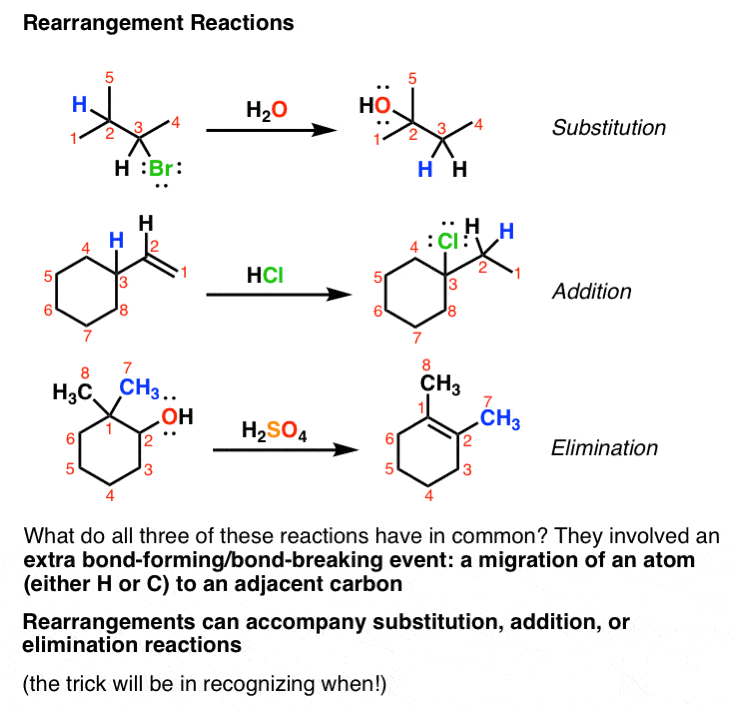
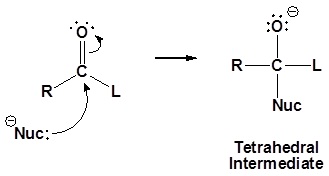
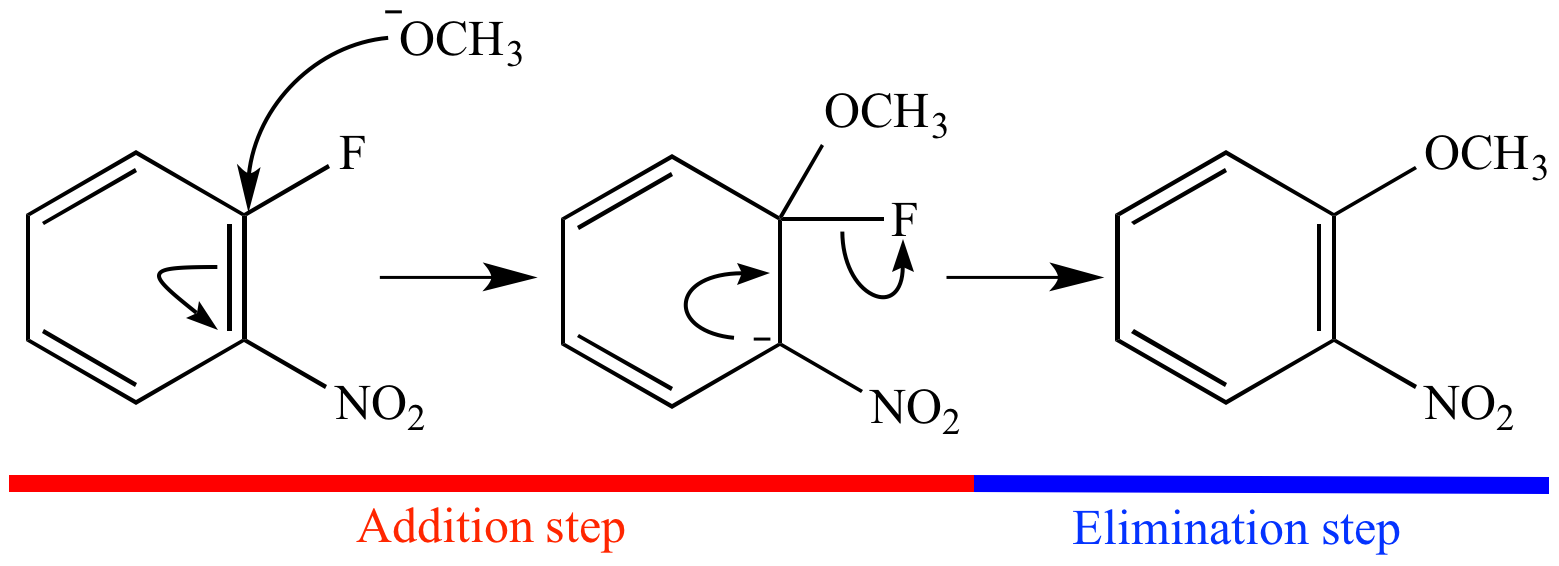
Nucleophilic addition – reaction of aldehydes and ketones C of C=O is delta positive (the most electrophilic centre). R groups are inductively donating. - ppt download

Chapter 20 - Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination Reactions 1: The General Mechanism Involving Strong Nucleophiles Flashcards & Practice Test | Quizlet
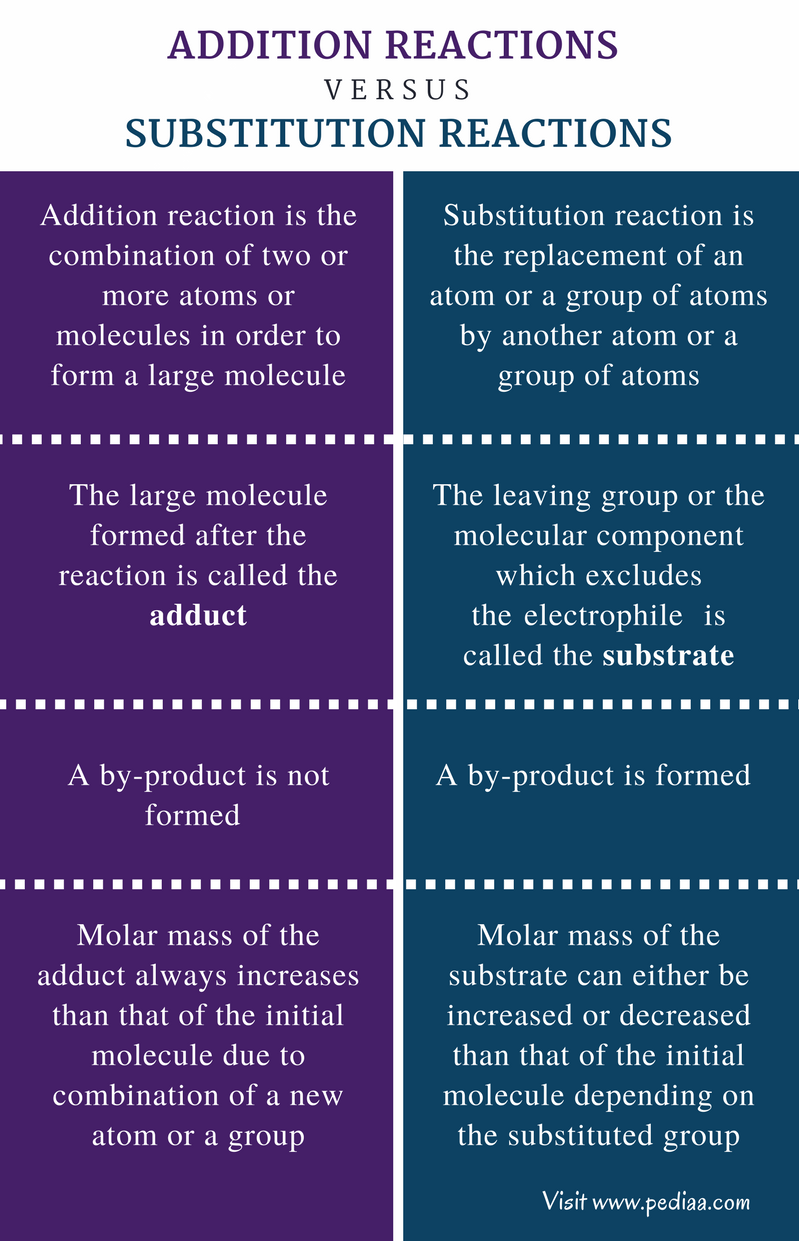
Difference Between Addition and Substitution Reactions | Definition, Types, Characteristics, Examples, Comparison

Which of the following would be most likely to undergo anucleophilic substitution reaction with aqueous sodiumhydroxide by an addition-elimination mechanism?(1} (3)(2) (4) | Snapsolve

organic chemistry - In the reversible reactions of acyl substitution, how do backward reactions happen by being against the forward reaction drives? - Chemistry Stack Exchange
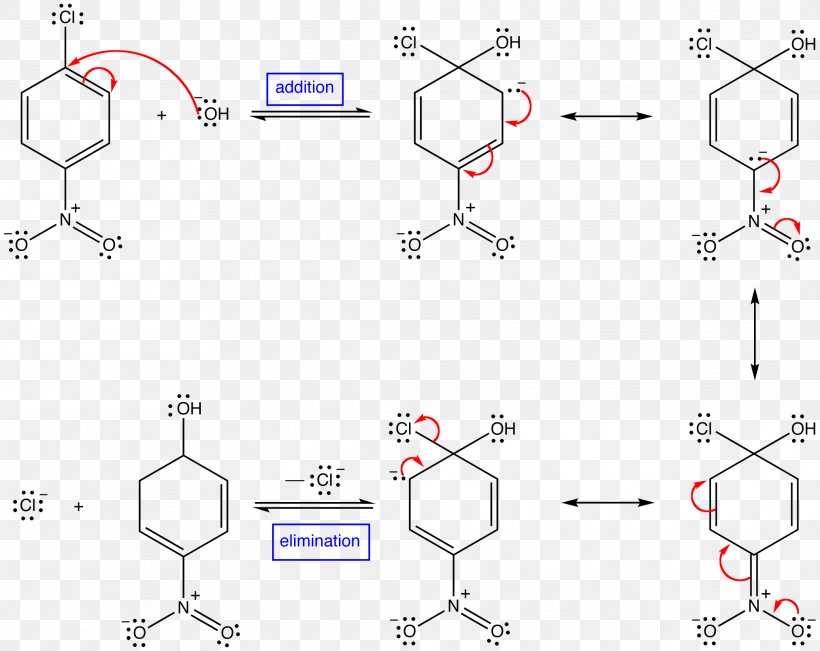
Addition Reaction Elimination Reaction Chemical Reaction Reaction Mechanism Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution, PNG, 2025x1608px, Addition Reaction, Acetoacetic
Solved] Select the major product of the following nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction that follows an addition/elimination mechanism. 1. OH... | Course Hero